Interior Design, Architecture, Residential, Residential Apartments
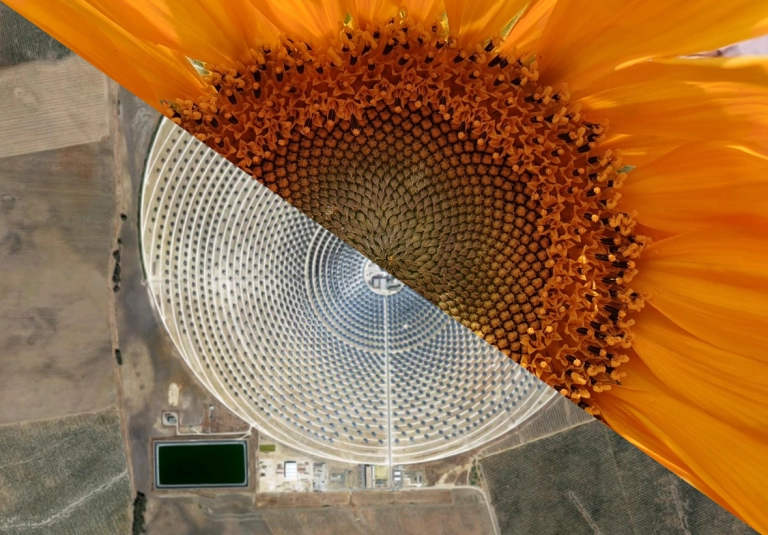
Biomimicry is the practice of taking inspiration from nature to solve human problems and design innovative solutions. From the shape of a bird’s wing to the structure of a spider’s web, nature has evolved highly efficient and sustainable solutions to the challenges it faces. Facets of Biomimicry seeks to learn from these natural systems and apply their principles to human design. In this blog post, we will explore seven key aspects of biomimicry.
Origins
The concept of Facets of Biomimicry has been around for centuries, with inventors and designers drawing inspiration from nature for centuries. However, it was biologist Janine Benyus who popularized the term “biomimicry” in her 1997 book of the same name. Since then, biomimicry has become a growing field of research and development.
Design principles
Biomimicry is based on a set of design principles that take inspiration from natural systems. These include using locally available materials, optimizing shape and form, and creating closed-loop systems that mimic natural cycles of resource use and waste disposal. By following these principles, designers can create more sustainable and efficient solutions.
Examples of biomimicry
There are countless examples of biomimicry in action. For example, the shape of the bullet train in Japan was inspired by the kingfisher bird, which can dive into water without creating a splash. The structure of a termite mound has inspired passive cooling systems in buildings. And the way that butterfly wings reflect light has inspired the creation of more efficient solar panels.
Biomimicry in materials science
Biomimicry is also being used in materials science to create new, sustainable materials. For example, scientists are studying the way that spider silk is created to develop new, strong and lightweight materials. The lotus leaf, which is highly water-resistant, has also inspired the creation of self-cleaning surfaces.
Biomimicry in medicine
Biomimicry is also being used in medicine to create more effective treatments. For example, the way that geckos can climb walls has inspired the development of adhesives that can be used to close wounds without the need for stitches. The way that the body’s immune system fights off infections is also inspiring new treatments for diseases.
Biomimicry and sustainability
Biomimicry is closely connected to sustainability, as it seeks to create solutions that are more efficient and less harmful to the environment. By taking inspiration from natural systems, designers can create solutions that use less energy and resources, produce less waste, and have a smaller environmental footprint.
Future of biomimicry
The field of biomimicry is still in its early stages, but its potential is enormous. As we face growing challenges around sustainability, climate change, and resource depletion, biomimicry offers a way to find innovative solutions to these complex problems. By learning from the natural world, we can create more efficient and sustainable systems that work in harmony with the environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 7 Facets of Biomimicry is a powerful tool that has the potential to transform the way we design and innovate. By taking inspiration from the natural world, we can create more sustainable and efficient solutions that work in harmony with the environment. As we face growing challenges around sustainability and resource depletion, biomimicry offers a way to find innovative solutions that can help us create a more sustainable future.
#NORAResidences #AvenirDevelopments #AvenirMeansFuture #Apartments #Biomimicry #NatureInspired #BiomimeticDesign #Bioinspiration #SustainableDesign #EcoEngineering #BiomimicryRevolution #BiologicalSolutions #InnovationFromNature #BiomimicryInspiration #BiomimicryPrinciples #NatureAsTeacher #BiomimeticSolutions #BiomimicryApplications #BiomimicryResearch #BiomimicryDesignThinking #NatureEngineering #BiomimicryForSustainability #BioInspiredDesign