Interior Design, Architecture, Residential, Residential Apartments, Bioclimatic Strategies
Introduction
In today’s world, where environmental concerns are at the forefront, architects and designers are exploring innovative ways to create sustainable built environments. Bioclimatic strategies offer a promising approach to address these challenges. By leveraging natural elements and passive design techniques, bioclimatic strategies aim to optimize the use of local climate conditions for energy efficiency, thermal comfort, and environmental harmony.
What are Bioclimatic Strategies?
Bioclimatic strategies refer to the design and planning techniques that harness the natural climate and environmental conditions to create comfortable, energy-efficient, and environmentally-friendly buildings. These strategies consider various factors such as solar radiation, wind patterns, temperature fluctuations, and precipitation levels, to name a few. By understanding and integrating these factors into the design process, architects can reduce the reliance on mechanical systems and minimize the overall environmental impact of buildings.
Benefits
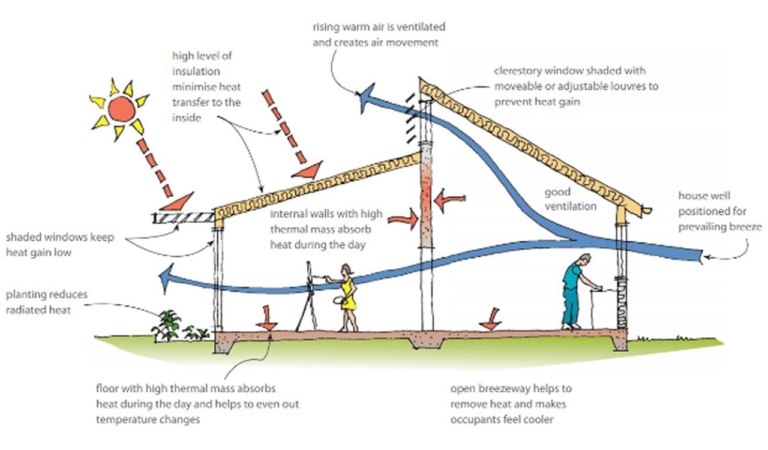
Implementing bioclimatic strategies offers numerous benefits, both for the occupants and the environment. Firstly, these strategies enhance thermal comfort by utilizing natural heating and cooling mechanisms. By optimizing insulation, thermal mass, and natural ventilation, buildings can maintain comfortable indoor temperatures throughout the year, reducing the need for excessive air conditioning or heating.
Secondly, bioclimatic strategies promote energy efficiency. Passive solar design techniques, such as proper orientation and maximizing sunlight exposure, help harness the sun’s energy for heating purposes during the winter while minimizing heat gain in the summer. This reduces reliance on artificial lighting and mechanical cooling systems, resulting in significant energy savings.
Passive Solar Design
One of the key components of bioclimatic strategies is passive solar design. This approach involves using the sun’s energy to heat and cool buildings naturally. Here are some important aspects of passive solar design:
-
Orientation and Sunlight
Proper building orientation plays a crucial role in passive solar design. By aligning the building’s layout with the path of the sun, architects can maximize solar gain in winter and minimize it in summer. This ensures optimal energy efficiency and thermal comfort.
-
Insulation and Thermal Mass
Effective insulation helps reduce heat loss during colder months and heat gain during hotter months. Thermal mass, such as concrete or stone, can absorb and store heat, helping to regulate temperature fluctuations inside the building.
-
Natural Ventilation
Incorporating natural ventilation systems, such as operable windows or vents, allows for the circulation of fresh air and the removal of excess heat. This helps maintain a comfortable indoor environment without relying solely on mechanical ventilation systems.
Green Roofs and Walls
Green roofs and walls are another strategy that offers several benefits. These features consist of vegetation coverings on building roofs or walls, providing insulation, reducing heat island effect, improving air quality, and supporting biodiversity. Green roofs also absorb rainwater, mitigating stormwater runoff and reducing the burden on drainage systems.
Shading and Sun Control
Effective shading techniques are crucial in bioclimatic design to minimize solar heat gain. Elements such as overhangs, louvers, or shading devices can be strategically positioned to block direct sunlight during peak hours while still allowing natural light to enter the building.
Water Conservation and Rainwater Harvesting
Bioclimatic strategies emphasize water conservation and rainwater harvesting. By implementing efficient plumbing fixtures, water-saving technologies, and collecting rainwater for non-potable use, buildings can reduce their water consumption and contribute to sustainable water management.
Efficient Lighting and Appliances
Incorporating energy-efficient lighting systems, such as LED or CFL bulbs, and selecting appliances with high energy ratings further enhance the overall energy efficiency of a building. These measures significantly reduce energy consumption, lower utility bills, and contribute to a greener environment.
Renewable Energy Integration
Bioclimatic strategies can also incorporate renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines. By integrating these technologies into the building design, renewable energy generation can offset the energy demands of the building and reduce reliance on fossil fuel-based power sources.
Bioclimatic Strategies in Different Climates
The application of bioclimatic strategies varies depending on the climatic conditions of a particular region. Here are some considerations for different climates:
-
Hot and Arid Climates
In hot and arid climates, strategies like passive cooling techniques, shading devices, and natural ventilation are crucial. Incorporating courtyard designs or utilizing evaporative cooling methods can help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
-
Hot and Humid Climates
In hot and humid climates, effective natural ventilation and humidity control are essential. Designing for cross ventilation, using breathable building materials, and incorporating dehumidification systems ensure a pleasant indoor environment.
-
Cold Climates
In cold climates, passive heating techniques take precedence. Proper insulation, air sealing, and maximizing solar gain through south-facing windows can significantly reduce the need for heating and minimize heat loss.
-
Moderate Climates
In moderate climates, a combination of passive cooling and heating techniques can be employed. This includes proper insulation, natural ventilation, and designing for solar gain based on the seasonal variations in temperature.
Case Studies
Several buildings around the world showcase the successful implementation of bioclimatic strategies. Examples include the Bahrain World Trade Center, which utilizes wind turbines to generate energy, and the Bullitt Center in Seattle, which incorporates passive solar design and rainwater harvesting.
Challenges and Limitations
While bioclimatic strategies offer numerous advantages, there are also challenges and limitations to consider. The effectiveness of these strategies heavily depends on the building’s design, site conditions, and user behavior. Additionally, retrofitting existing buildings to incorporate bioclimatic features can be complex and costly.
Future Trends
The field of bioclimatic strategies continues to evolve with advancements in technology and a greater focus on sustainable development. Future trends may include the integration of smart building systems, advanced energy monitoring and management tools, and the use of innovative materials with improved insulation and energy-saving properties.
Conclusion
Bioclimatic strategies play a crucial role in creating sustainable built environments that prioritize energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and environmental stewardship. By leveraging natural elements and passive design techniques, architects and designers can reduce the carbon footprint of buildings and contribute to a greener future.
FAQs
What are bioclimatic strategies?
- Bioclimatic strategies are design and planning techniques that utilize the natural climate and environmental conditions to create sustainable and energy-efficient buildings.
How do bioclimatic strategies benefit the environment?
- Bioclimatic strategies promote energy efficiency, reduce reliance on mechanical systems, and minimize the overall environmental impact of buildings.
What is passive solar design?
- Passive solar design involves harnessing the sun’s energy for heating and cooling purposes through techniques like proper orientation, insulation, and natural ventilation.
How do bioclimatic strategies vary in different climates?
- Bioclimatic strategies adapt to different climates by employing specific techniques to optimize thermal comfort and energy efficiency based on regional climatic conditions.
What are some challenges of implementing bioclimatic strategies?
- Challenges include design complexities, retrofitting existing buildings, and ensuring user compliance and behavior for optimal performance.
#NORAResidences #AvenirDevelopments #AvenirMeansFuture #Apartments #GreenBuildingDesign #SustainableArchitecture #ClimateResponsive #PassiveDesign #BioclimaticSolutions #EnergyEfficiency #NaturalVentilation #GreenRoofs #SolarShading #EnvironmentalPerformance